my cheat sheet on IOS-XE API
1 IOS-XE
Runs on Catalyst switches and enterprise routers. Is modular, built on Linux. It enables "Intent Based Networking IBN" networking through DNA-Center, a s/w centric, policy driven, automated network.
Supports three operational approaches to programmatically integrate a network element:
- via a controller for example DNA-Center
- via configuration mgt toos (i.e. DevOps)
- includes Ansible, Puppet, Chef
- directly via cli
See also Automating Device Operational Life Cycle file.
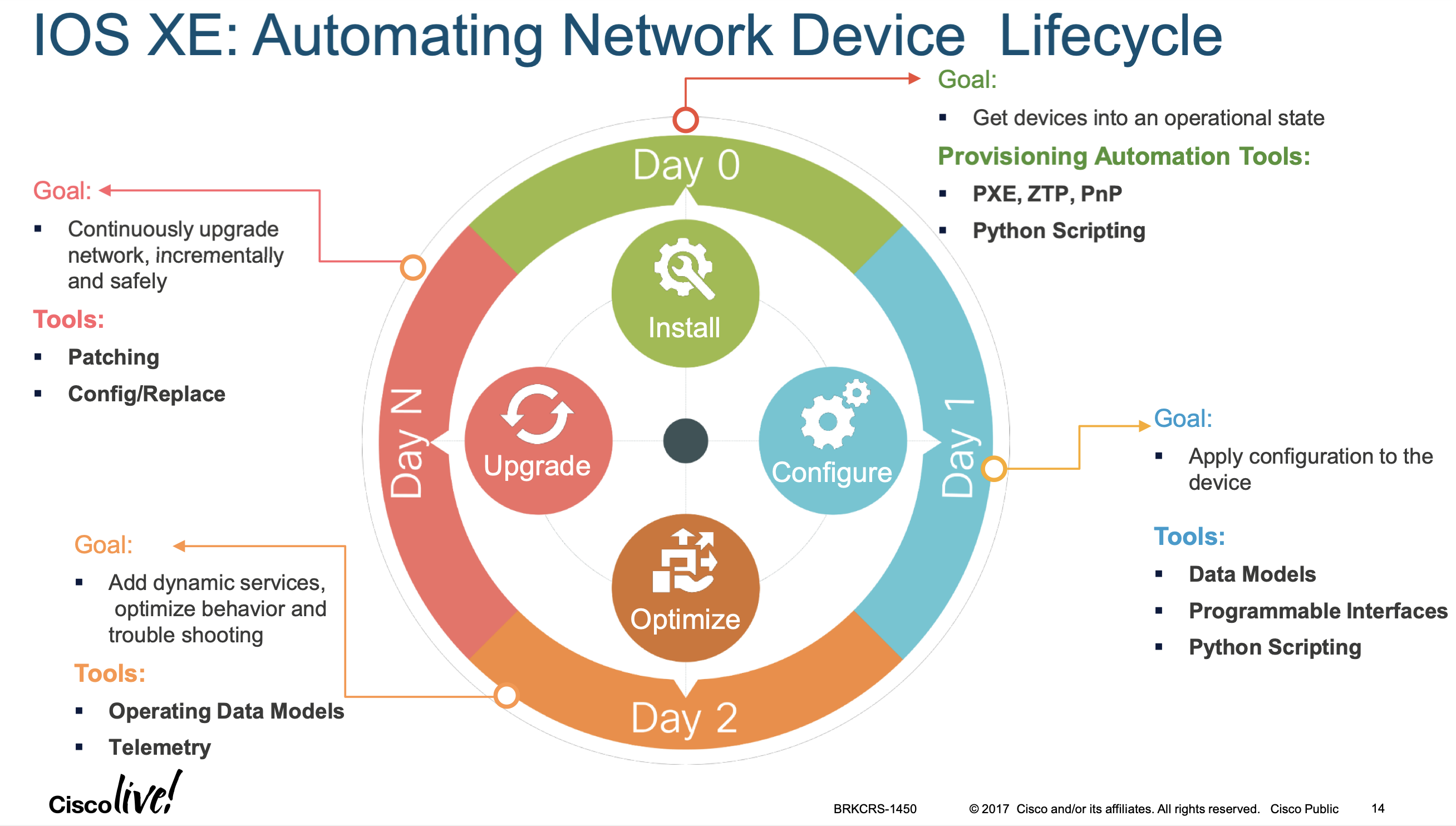
As well as:

Controllers usually expose a northbound REST API, while their southbound APIs may be proprietary. But the user never sees that anyway.
DNA-C controller is designed to provide a closed-loop feedback, allowing the
controller to dynamically adjust network configurations based on the changing
network context.
1.1 config mgt tools
- enable DevOps workflows access to the full feature set of the device.
- changes are "modelled" and validated in a simulated environment prior to deployment to production.
- these tools can also mange compute and app resources.
- not
closed loop feedbackthough, hence you need to validate changes extensively using simulation tools prior to deployment. - validation testing and configuration pushes are orchestrated through continuous integration tool chains, CI/CD.
DIY tools usually directly controls each network element through some scrits. Good for a few devices, but does not scale. Direct integration works for monitoring dvides and ensuring changes did not create undesired states.
1.2 IOS-XE config protocols
- RESTCONF (json)
- NETCONF (xml)
2 IOS-XE APIs
Model driven in both open models and native models
open modelsyang models from vendors, ietf, openconfig groupnative modelsrepresent a model-based interface of current cli device operation. closest to the feature implementation of the device.
(remember nx-os has mit models, as well as yang models, and openconfig models) ios-xe only has yang model

2.1 NETCONF on IOS-XE
Initially only supported CLI commands over NETCONF, but now implemented a
full YANG model, so now NETCONF on IOS-XE is robust and native XML objects
can be sent and received.
| Layer | Example |
|---|---|
| Transport | SSHv2 |
| Protocol | |
| RPC | <rpc>, <rpc-reply> |
| Operations | <get-config>, <get>, <copy-config>, <commit>, <validate>, |
| <lock>, <unlock>, <edit-config>, <delete-config> | |
| Content | XML representation of YANG models. |
2.2 IOS-XE Datastores:
IOS-XE supports two:
- running
- candidate
Also supports locking these two data stores, and config roll-back
2.3 RESTCONF on IOS-XE
RESTCONF just like any other REST API, except that RESTCONF demands you use specific headers, and that URL and data is driven by YANG models.
application/vnd.yang.data+jsonfor JSONapplication/vnd.yang.data+jsonfor JSONapplication/vnd.yang.data+xmlfor XMLapplication/vnd.yang.data+xmlfor XML
Constructing a URL for RESTCONF is the same as you would for REST APIs. You need to understand the:
- methods
- entry points
- resources
- queries
2.4 gNMI on IOS-XE
The Google developed gRPC Network Management Interface (gNMI) lets you
- install
- manipulate
- delete
configuration data on a device, as well as:
- view operational data
The content viewed using gNMI can be modeled using YANG, and uses JSON encoding for the data.
3 Python on IOS-XE
3.1 On box:
Has a python interpreter included in the IOS-XE Guest Shell. Scripts can perform:
- provisioning automation (PoAP, PnP, PXE python scripts)
- automating EEM
- application development
- IOT
3.2 Off box:
ssh/netconfis used to connect to the device- will need to authenticated access to the device
Scripts can perform:
Config mgt automation(anything you can do with "config t" can be automated using off-box python scripts with NETCONF)telemetryand operation dataretrieval(new feature is model-driven telemetry, where data is streamed from the devicecontinuously, in apushmodel. You getnear-real-timeaccess to operational statistics.- controller based automation, via DNAC and Cisco Network PnP. (saves you the trouble of doing box by box automation, and lets the controller do the minutiae)
- IOT off-box automation handles IoT device connectivity mgt and deployment automation, and monitoring.
3.3 IOS-XE Guest Shell
Running on the IOS-XE device is a built-in Linux container, LXC, with python2
installed. Extra python libraries can be added, such as requests, ncclient,
xml.etree.ElementTree. Supports Day0 device onboarding. Is isolated from
IOS-XE processes, so they are protected and safe, from a h/w processor and
memory perspective. However the storage is shared between them both, i.e.
flash: usbflash0: etc. Use the IOS-XE commands: show file systems and
dir /all or just dir to see what file systems are on the router.
4 ios-xe sdk
cisco offers these toolkits for ios-xe programmability:
yang suite(was yang explorer) where you interact with a yang server s/w typically run on your laptop, that then can download yang models directly from your network device. see: YANG Suite file.pyangis an opensource python library developed by Cisco.*ncclientis an opensource python library
To turn on netconf-yang on an IOS-XE device, config t:
netconf-yang
*